What is image binarization?
2023-07-17WIKI
Image binarization is a process that converts the color or grayscale original captured images into digital binary images consisting of small black and white pixels. Image binarization is the basis of image analysis and is the key step in image processing used for particle identification.
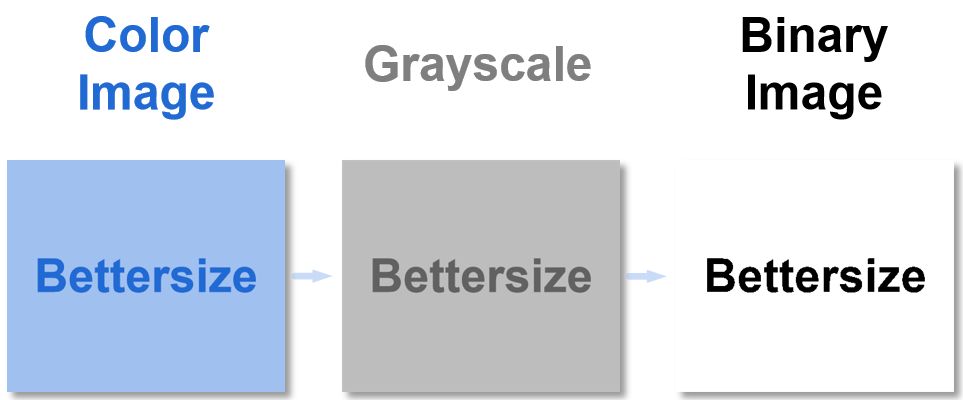
The measurement system provides two image binarization methods called automatic image binarization and double-threshold image binarization. Automatic image binarization is a binarization threshold determination method with which the binarization threshold is formulated automatically based on the original image.
In addition to the automatic image binarization, users are allowed to use double-threshold image binarization to highlight the pixels within a specific range of pixel values. In double-threshold image binarization, only pixels whose pixel values are larger than or equal to the minimum threshold and lower than the maximal threshold will be identified as bright pixels. Other pixels will be recognized as dark pixels. An example is shown below. The binarization process varies with modified thresholds.

Recommended articles
Related Particle Size Analyzer
-
Bettersizer S3 Plus
Laser Diffraction Particle Size Analyzer
Measurement range: 0.01 - 3,500μm (Laser System)
Measurement range: 2 - 3,500μm (Image System)
-
BeVision D2
Image Analyzer
Dispersion type: Dry
Measurement range: 30 - 10,000μm
Technology: Dynamic Image Analysis
-
BeVision M1
Automated Static Image Analyzer
Dispersion type: Dry
Measurement range: 0.3 - 10,000 μm
Technology: Static Image Analysis
-
BeVision S1
Classical and Versatile Static Image Analyzer
Dispersion type: Dry & Wet
Measurement range: 0.3 - 4,500 µm
Technology: Static Image Analysis