- ● Introduction
- ● Particle size and shape analyzer
- ● Merits
- ● Measurement principle
- ● Supplementary Information
Introduction
Particle size and shape parameters can be precisely obtained using dynamic image analysis (DIA), which provides a feasible method for the in-depth study of particle size and shape. When compared to static image analysis (SIA), DIA continuously captures images of the particles during the flow and then analyzes them to determine particle size and shape parameters. This analysis measures both suspended and free-falling particles as well as those that are inclined to agglomerate.
Particle size and shape analyzer

Bettersizer S3 Plus
Particle Size and Shape Analyzer
Measurement range: 0.01 - 3,500μm (Laser System)
Measurement range: 2 - 3,500μm (Image System)

BeVision D2
Dynamic Image Analyzer
Dispersion type: Dry
Measurement range: 30 - 10,000μm
Technology: Dynamic Image Analysis
1. Easier operation and lower susceptibility to human errors
2. Oversized particle sensitivity
3. Quick and efficient analysis
4. High sample throughput
5. Highly representative and accurate results
Measurement Method
Four steps to determing the particle shape and size by DIA:
1. Image capturing
The image is taken by special digital cameras to enlarge the particle while avioding the motion blur, usually combined with a microscope. The particles are present in motion, and the deagglomeration of particles is possible both in dry and wet mode.
2. Image processing and particles identification
Appropriate software processing results in enhanced images, realizing the elimination of isolated pixels and edging particles, the retouching of variations in brightness and signal noise, and the separation of agglomerated particles.
3. Particles size and shape parameters calculation
Size and shape parameters of every single particle will be calculated with the software.
4. Data statistics and classification
The particles are classified based on their size and shape parameters.
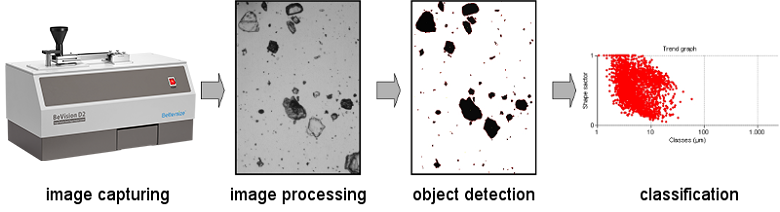
Processing chain


