Research on Particle Size Measurement of Chinese Medicine Powder by Laser Particle Size Analyzer
2021-07-12Application Note
Particle size and its distribution are crucial for Chinese medicine powder quality and drug safety, but irregularity often causes varied measurement results. Laser particle size measurement offers a fast, wide-ranging, and reproducible solution. This paper explores its principles, characteristics, and application in Chinese medicine powder analysis.
| Product | Bettersizer 2600 |
| Industry | Pharmaceuticals |
| Sample | Poria cocos, Astragalus membranaceus, Angelica sinensis, Salvia miltiorrhiza, Codonopsis pilosula, Dendrobe, Momordica grosvenori |
| Measurement Type | Particle Size |
| Measurement Technology | Laser Diffraction |
Jump to a section:
Abstract: Objective: To establish a laser diffraction method for the determination of particle size distribution of Chinese medicine powders. Method: Using Bettersizer 2600, an automatic laser diffraction particle size analyzer with both dry and wet dispersion system, to systematically study the particle size distribution of different Chinese medicine powders. The research investigated the impact of dispersing intensity on the particle size analysis, including different air pressures of dry dispersion and different stirring speeds and ultrasonic dispersing time of wet dispersion.
Conclusion: By comparing the measurement results, it is concluded that dry dispersion can better control risks and provide more reasonable data correlation.
Key words: Laser diffraction; Particle size analyzer; Chinese medicine
Traditional Chinese medicine powder is one of the most important forms of Chinese medicinal materials. For example, pills and powders are forms mixed by one or more medicinal powder. According to particle size, Chinese medicine powder can be divided into traditional powder, micron powder, and nano-powder. With the continuous improvement of drug processing and detection technology, the research of Chinese medicine powder has been developed rapidly. The traditional Chinese medicine is prepared into herbal medicine granule, micron medicine and nanometer medicine. By reducing the particle size, the specific surface area of drug particles can be increased and the solubility and bioavailability of traditional Chinese medicine are improved.
The properties of Chinese medicine powder have great influence on the forming process. The particle size and particle size distribution, which are related to the quality of the products and the safety of the drugs, are the important physical properties of the Chinese medicine powder. However, because of the irregularity and inhomogeneity of particle size, the results obtained by different measurement methods are different. Laser particle size measurement has been widely used in the determination of traditional Chinese medicine by its fast measuring speed, wide measurement range, and good reproducibility. This paper focused on the principles and characteristics of laser diffraction particle size measurement and its application of Chinese medicine powder.
The CHP and the USP have clear regulations on raw materials particle sizing by laser diffraction method, such as the structure and principle of the instrument, the specific method of dry and wet dispersions, the factors in the measurement process, etc. However, for specific Chinese medicine, there is no related instruction on how to choose between dry and wet dispersion methods and how to evaluate the measurement results. This paper carried out a systematic research on Chinese medicine particle size distribution measurement in accordance with the USP and the ISO 13320.
1. Experiment
1.1 Instruments0
- Bettersizer 2600 laser particle size analyzer from Bettersize Instrument Ltd;
- MS303S electronic scale from Mettler Toledo;
- SC ultrasonic cleaner from Shanghai Shengyan Ultrasonic Instrument Co., Ltd.
1.2 Sample and reagent
Seven kinds of Chinese medicine powder samples:
- Poria cocos
- Astragalus membranaceus
- Angelica sinensis
- Salvia miltiorrhiza
- Codonopsis pilosula
- Dendrobe
- Momordica grosvenori
2. Particle size distribution measurement and method evaluation
2.1 Dry dispersion method
2.1.1 Study on the methodology of dry dispersion method
Dry dispersion is to transport powder particles by compressed air, disperse powder particles by collision of particles and particles, collision of particles and pipe, and airflow shear.
Drug powder was composed by small organic molecules particles, which could break under the shear stress and collision. In order to ensure the dispersal of large agglomerate without breaking the original particles, the USP requires investigating the effect of different dispersive intensity on measurement results (USP 429):

In dry dispersion experiments, we investigated the effect of dispersed pressure on the particle sizing results. The dispersed pressure ranged from 0.05 MPa to 0.25 MPa (Figure 1-7).
Abscissa: dispersion pressure; Ordinate: particle size; Blue
curve: D10; Orange curve: D50; Grey curve: D90.
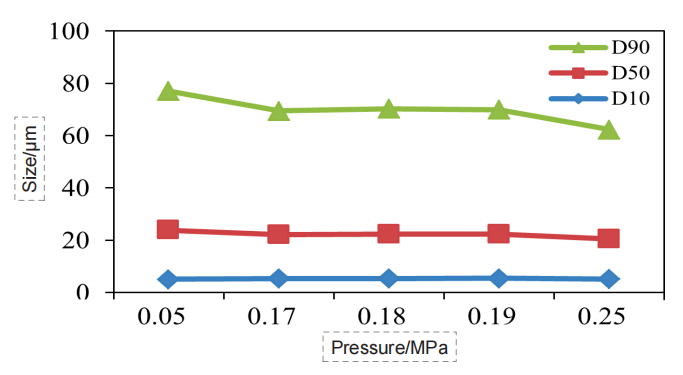
Figure 1. Particle size pressure titration data of Poria cocos sample (dry dispersion)
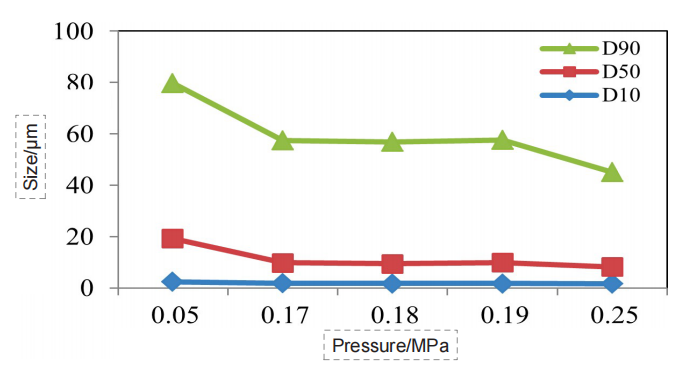
Figure 2. Particle size pressure titration data ofAstragalus membranaceus sample (dry dispersion)
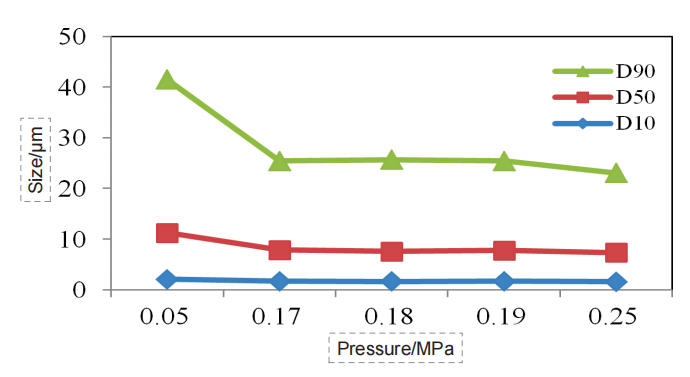
Figure 3. Particle size pressure titration data ofAngelica sinensis sample (dry dispersion)
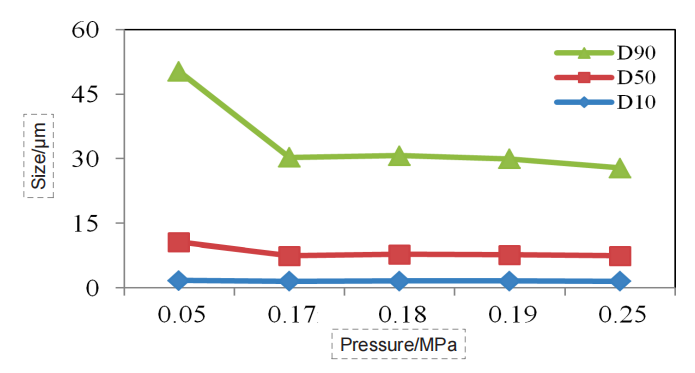
Figure 4. Particle size pressure titration data of Salvia miltiorrhiza sample (dry dispersion)
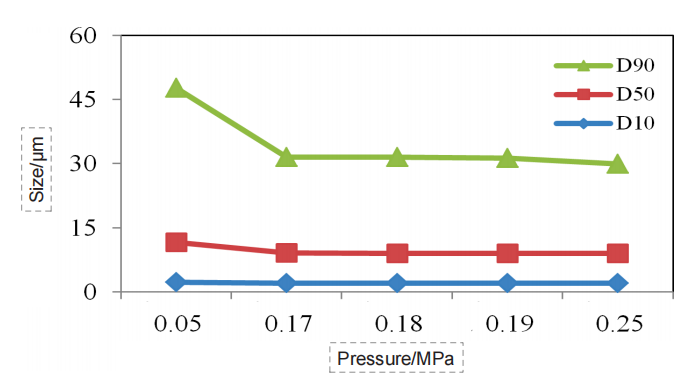
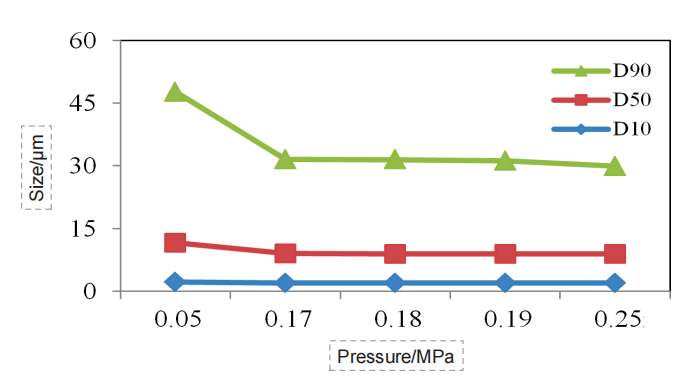
Figure 6. Particle size pressure titration data of Dendrobe sample (dry dispersion)
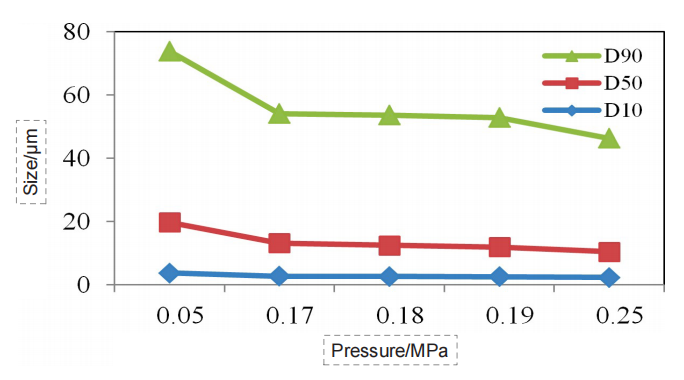
Figure 7. Particle size pressure titration data of Momordica grosvenor sample (dry dispersion)
the ideal pressure titration curve, as the dispersed pressure increases, the particle size gradually decreases, and the curve gradually reaches a stable period. If pressure increases further, the curve will go further downward, which corresponds to the gradual dispersal of large agglomerate to single particles. If the pressure is further increased, the drug particles could break.
Through the pressure titration of the seven kinds of Chinese medicine, we can see that the overall data conformed to the above rules, all of which were decreased with the pressure increase first, then gradually reached a “stable platform”, and the second decline might occur at the end. Although some drugs did not have the second drop, such as Dendrobe, we could basically determine that the risk of data was low under the 0.18 MPa dispersion pressure.
2.1.2 Research of the precision of dry dispersion method
Based on the above conditions, we investigated the precision of the particle size under dispersion pressure of 0.18 MPa. The repeatability results for seven samples were excellent: the relative standard deviation of D50 was less than 1%, and those of D10 and D90 data were also below 2%, which meets the requirements of the CHP and the USP, indicating that the dry dispersion results were relatively reliable.
According to the results of particle size distribution, the difference of each Chinese medicine is relatively large. The smallest D50 is about 5 µm, and the largest one can reach 16 µm; the minimum of D90 is 19 µm, and the maximum is nearly 50 µm.
| Sample |
D10/µm
|
D50/µm
|
D90/µm
|
D95/µm
|
|
Poria cocos-0.18-3
|
5.396 | 16.95 | 47.9 | 64.61 |
| Poria cocos-0.18-2 | 5.449 | 16.99 | 48.11 | 64.87 |
| Poria cocos-0.18-1 | 5.462 | 16.83 | 47.66 | 64.29 |
| RSD | 0.64% | 0.49% | 0.47% | 0.45% |
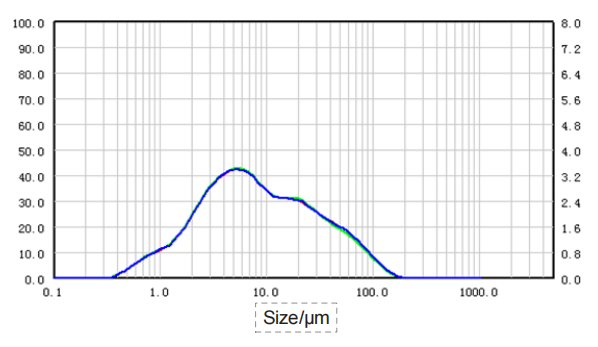
| Sample |
D10/µm
|
D50/µm
|
D90/µm
|
D95/µm
|
|
Astragalus-0.18-3
|
1.709 | 7.671 | 47.530 | 68.74 |
| Astragalus-0.18-2 | 1.692 | 7.521 | 45.410 | 66.50 |
| Astragalus-0.18-1 | 1.708 | 7.669 | 47.560 | 68.74 |
| RSD | 0.56% | 1.13% | 2.63% | 1.90% |
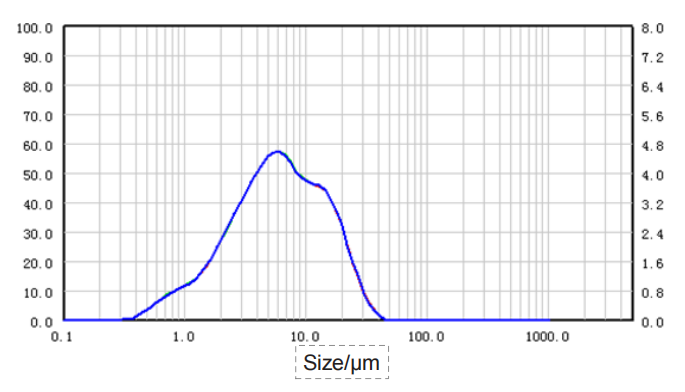
| Sample |
D10/µm
|
D50/µm
|
D90/µm
|
D95/µm
|
|
Angelica sinensis-0.18-3
|
1.627 | 5.963 | 18.070 | 22.41 |
| Angelica sinensis-0.18-2 | 1.624 | 5.965 | 18.070 | 22.41 |
| Angelica sinensis-0.18-1 | 1.627 | 5.960 | 18.070 | 22.41 |
| RSD | 0.11% | 0.04% | 0.00% | 0.00% |
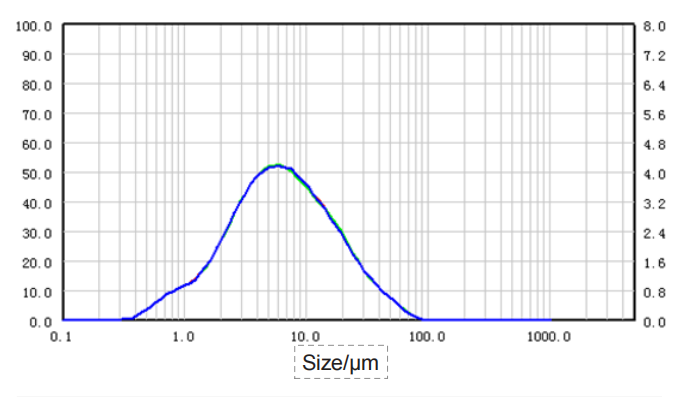
| Sample |
D10/µm
|
D50/µm
|
D90/µm
|
D95/µm
|
|
Salvia miltiorrhiza-0.18-3
|
1.634 | 6.186 | 22.880 | 32.180 |
| Salvia miltiorrhiza-0.18-2 | 1.638 | 6.193 | 23.000 | 32.250 |
| Salvia miltiorrhiza-0.18-1 | 1.637 | 6.190 | 22.920 | 32.250 |
| RSD | 0.13% | 0.06% | 0.27% | 0.13% |
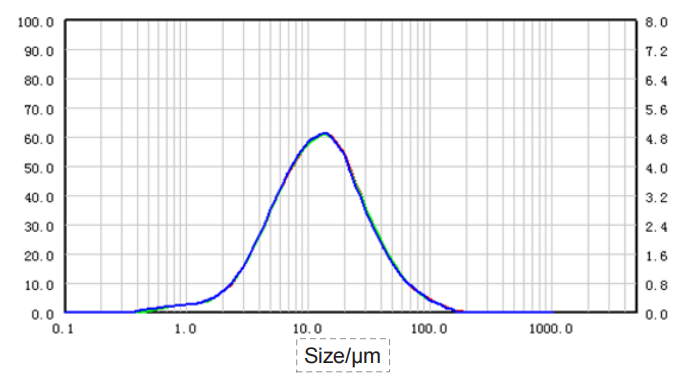
| Sample |
D10/µm
|
D50/µm
|
D90/µm
|
D95/µm
|
|
Codonopsis pilosula-0.18-3
|
3.888 | 12.500 | 38.030 | 53.250 |
| Codonopsis pilosula-0.18-2 | 3.887 | 12.470 | 38.210 | 53.240 |
| Codonopsis pilosula-0.18-1 | 3.813 | 12.300 | 37.750 | 53.050 |
| RSD | 1.11% | 0.87% | 0.61% | 0.21% |
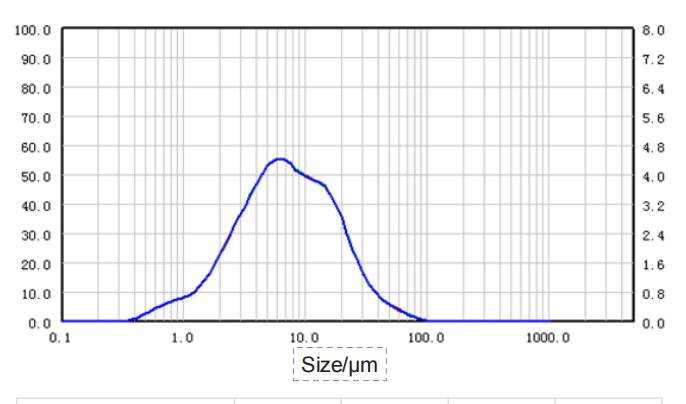
| Sample |
D10/µm
|
D50/µm
|
D90/µm
|
D95/µm
|
|
Dendrobe-0.18-3
|
1.994 | 6.995 | 22.470 | 29.970 |
| Dendrobe-0.18-2 | 1.992 | 6.992 | 22.460 | 29.930 |
| Dendrobe-0.18-1 | 1.994 | 7.000 | 22.500 | 30.020 |
| RSD | 0.06% | 0.06% | 0.09% | 0.15% |
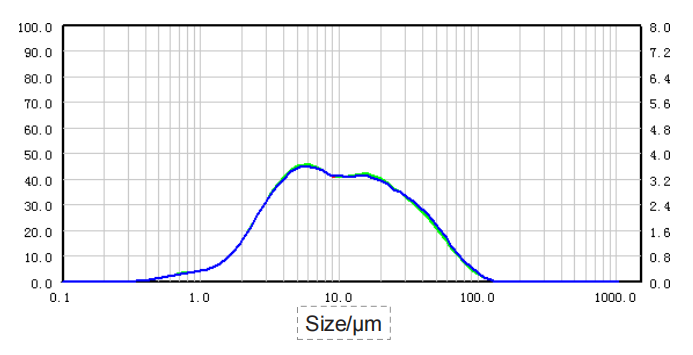
| Sample |
D10/µm
|
D50/µm
|
D90/µm
|
D95/µm
|
|
Momordica grosvenori-0.18-3
|
2.589 | 9.787 | 40.58 | 53.98 |
| Momordica grosvenori-0.18-2 | 2.581 | 9.694 | 39.96 | 53.43 |
| Momordica grosvenori-0.18-1 | 2.596 | 9.836 | 41.23 | 54.66 |
| RSD | 0.29% | 0.74% | 1.56% | 1.14% |
2.2 Wet dispersion method
The solubility of the Chinese medicine is poor with water. Besides, its powder density is small and tends to float on water. Therefore, we adopted a compound surfactant to improve the dispersity of the powder in the water. The dispersion effect was as follows:

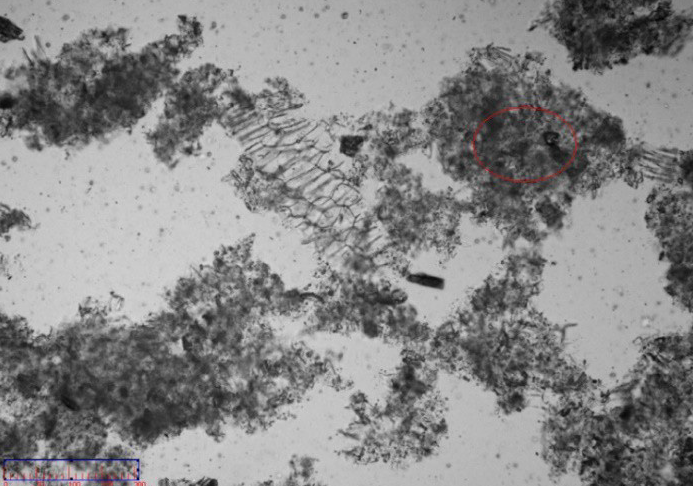
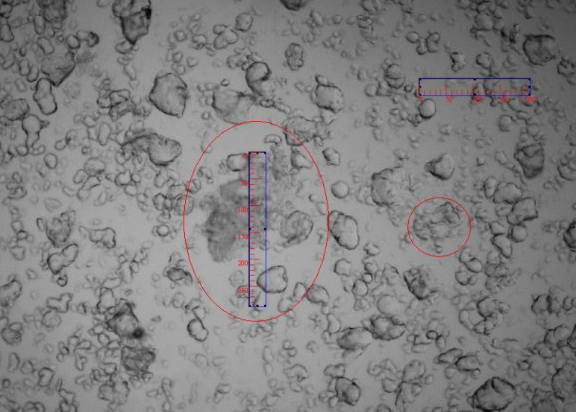
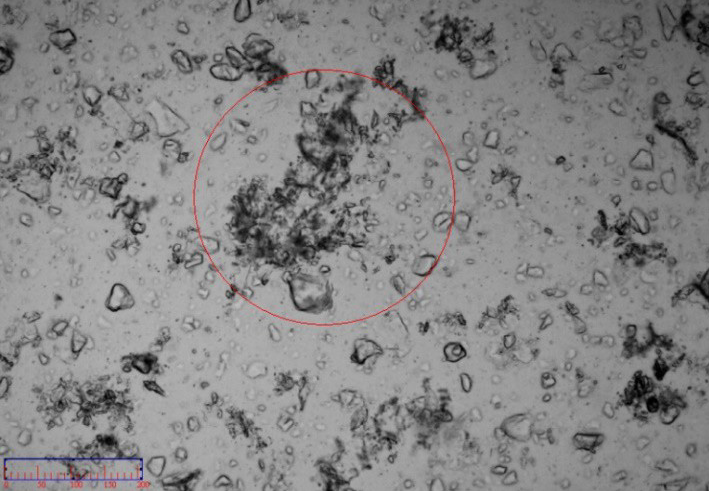
Although the compatibility of the Chinese medicine powder could be improved by the surfactant and the dispersion of the powder could be improved by ultrasonic, due to the characteristics of the Chinese medicine, the dispersion of the powder in water was in forms of mass and flocculation. Although some special solvents could improve the dispersing effect, it is difficult to find one kind of solvent to disperse a variety of Chinese medicine powder.
3. Conclusion
Generally, the laser diffraction particle size analyzer with dry dispersion method can provide high precision particle size distribution result of Chinese medicine powder. Although wet dispersion method can disperse the powder through surfactants and ultrasonic, the effect is not satisfied.
Therefore, dry dispersion method is relatively reasonable to analyze particle size distribution of Chinese medicine powder.
About the Author
| Dr Xuebing Li, Shiqi Liu, Mei Li, Liuyang Xu Engineers @ Application Research Lab, Bettersize Instruments |
Recommended articles
Rate this article
