Why do we use equivalent spherical diameter?
2023-07-12WIKI
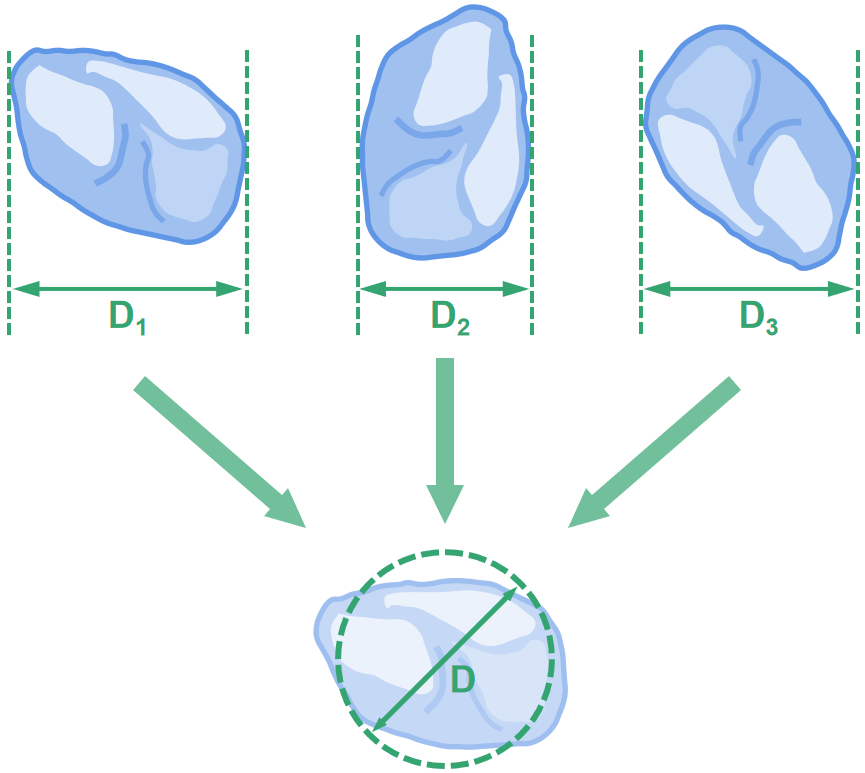
For perfect spheres, diameter can be used as a measure to describe their size. Real-world particles are characterized by their irregularities, resulting in several different size descriptions that could validly be used but with some difficulty. The equivalent spherical diameter was introduced as a valid base with which results from different techniques could be harmonized to facilitate and unify the illustration. The D shown below is the equivalent spherical diameter, which is not the largest or smallest diameter measured when interacting with the laser but can be the average of the sum of all that particle’s orientations towards the laser.
Recommended articles
Related Particle Size Analyzer
-
Bettersizer S3 Plus
Laser Diffraction Particle Size Analyzer
Measurement range: 0.01 - 3,500μm (Laser System)
Measurement range: 2 - 3,500μm (Image System)
-
Bettersizer ST
One-stop Particle Size Analyzer
Dispersion type: Wet
Measurement range: 0.1 - 1,000µm
Repeatability: ≤1% variation
-
Bettersizer 2600
Particle Size Analyzer
Measurement range: 0.02 - 2,600μm (Wet dispersion)
Measurement range: 0.1 - 2,600μm (Dry dispersion)






