How to calculate mean particle size with a stability analyzer?
2024-09-24WIKI
Mean particle size analysis can be carried out with a stability analyzer based on three methods: gravitational liquid sedimentation, transmission, and backscattering. The relationship between the sedimentation velocity and mean particle size is the key to the gravitational liquid sedimentation method. This method can be applied to samples with relatively large particles that tend to settle down. The transmission method is based on Beer-Lambert law, which is suitable for clear, diluted samples with small particle size. The backscattering method is deduced from Mie theory and it is suitable for samples with small particle size, proper concentration, and strong backscattering. Additional parameters that are related to samples are also necessary for the calculation.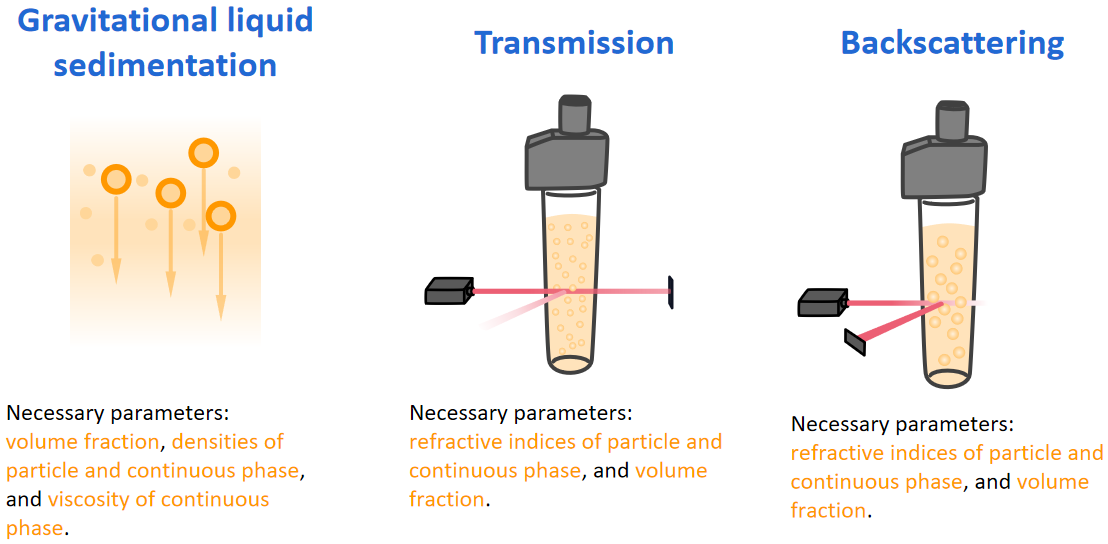
Recommended articles
Related Particle Size Analyzer
-
BeScan Lab
Stability Analyzer
Particle size ranges from 10 nm to 1 mm
Volume fraction up to 95%
Compliance with ISO/TR 18811, 13097, 21357, 22107




