How are particles dispersed when using the wet method?
2022-11-29WIKI
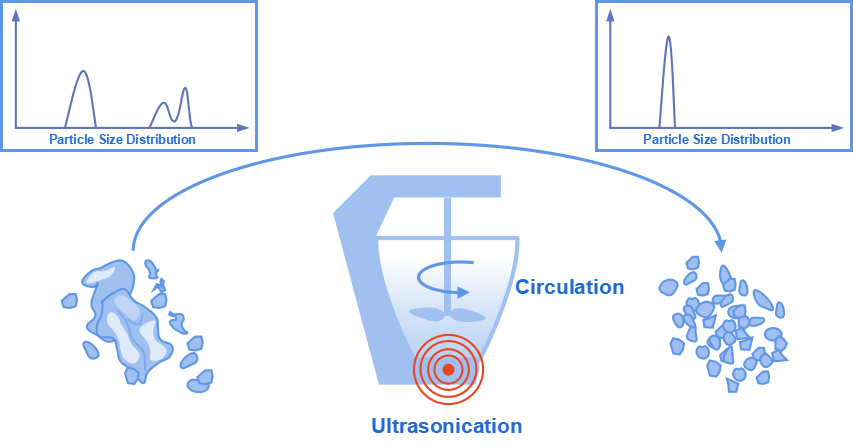
In laser diffraction particle size analysis, inaccurate results can be caused by particle agglomerating in the suspension, especially when they are fine. Therefore, a full dispersion of the sample prior to measurement is essential.
Three effective methods are available for the sample dispersion when using the wet method. Primary dispersion of aggregates can be achieved by circulating the suspension through a wet flow path containing a stirring blade. In addition, variable levels of ultrasonication can be helpful in deagglomeration. Thirdly in some systems, the downward slope of the circulation tank and a higher pump speed can effectively prevent the precipitation of particles with a higher specific gravity or larger particle size in the wet flow path, leading to a complete dispersion and hence a statistically good representation of the particles. For particles that float on the meniscus of the water, an appropriately diluted surfactant may be necessary to lower the surface tension. Hence the particles can be absorbed into the water.
Recommended articles
Related Particle Size Analyzer
-
Bettersizer S3 Plus
Laser Diffraction Particle Size Analyzer
Measurement range: 0.01 - 3,500μm (Laser System)
Measurement range: 2 - 3,500μm (Image System)
-
Bettersizer ST
One-stop Particle Size Analyzer
Dispersion type: Wet
Measurement range: 0.1 - 1,000µm
Repeatability: ≤1% variation
-
Bettersizer 2600
Particle Size Analyzer
Measurement range: 0.02 - 2,600μm (Wet dispersion)
Measurement range: 0.1 - 2,600μm (Dry dispersion)






