Determining Lentinan Molecular Weight Using the BeSEC
2026-01-15Application Note
Abstract: Lentinan is a bioactive polysaccharide whose molecular weight strongly influences its immunomodulatory and functional properties. In this study, size-exclusion chromatography coupled with static light scattering and refractive index detection was employed to determine the absolute molecular weight and molecular weight distribution of lentinan samples, enabling clear differentiation among grades and supporting application-specific selection.
Keywords: Lentinan, Polysaccharide, Absolute molecular weight, Molecular weight distribution, Size-exclusion chromatography (SEC), Static Light scattering
| Product | BeSEC |
| Industry | |
| Sample | Lentinan (polysaccharide extracted from shiitake mushrooms) |
| Measurement Type | Absolute molecular weight and molecular weight distribution |
| Measurement Technology |
Size-Exclusion Chromatography (SEC), Static Light Scattering
|
Introduction
Lentinan is a bioactive polysaccharide extracted from shiitake mushrooms, widely recognized for its immunomodulatory effects. It is commonly used as an adjuvant in cancer therapy to ease the side effects of chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Beyond oncology, lentinan exhibits antiviral and antioxidant activity and is frequently incorporated into health supplements to enhance immunity and slow aging. In food applications, it improves texture and stability while adding nutritional value.
Molecular weight plays a critical role in lentinan’s functionality. Higher molecular weight molecules tend to adopt more ordered structures and bind more effectively to immune cell receptors, resulting in stronger immunomodulatory effects. Lower molecular weight molecules dissolve and absorb more easily, but their biological activity may be shorter-lived.
Selecting the appropriate molecular weight is essential for optimizing performance in specific applications.
Experimental Section
This study utilized a Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC) system equipped with refractive index (RI) and light scattering (LS) detectors. The light scattering detector is the BeSEC LS2 from Bettersize Instruments, with 90° and 7° angles. The BeSEC workstation combines light scattering with RI or UV signals to calculate molecular weight averages (Mn, Mw and Mz) and distributions.
System Configuration:
- Detectors: Light Scattering (LS) + Refractive Index (RI)
- Column: Shodex Ohpak LB-806M
- Mobile phase: 0.05 M NaNO3 aqueous solution
- Flow rate: 0.7 mL/min
- Injection volume: 100 μL
- Column temperature: 40 ℃
- dn/dc: 0.129 mL/g
Sample Preparation:
Five lentinan samples were analyzed. Each powder was accurately weighed and dispersed in 0.05 M NaNO3, stirred until clear (1 to 3 mg/mL), filtered through a 0.22 μm PES syringe filter, and transferred into vials and placed in the autosampler for measurement.
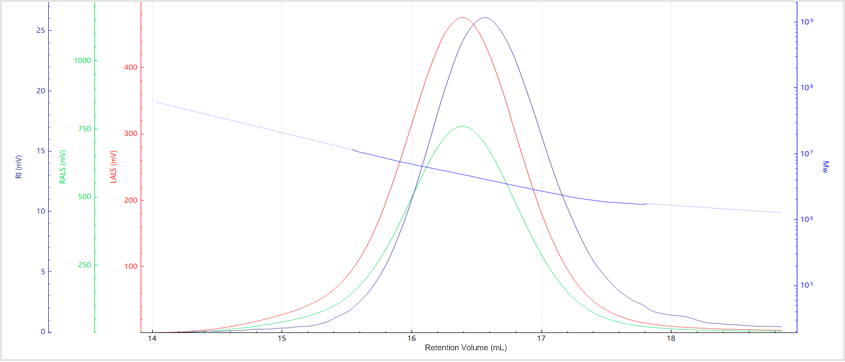
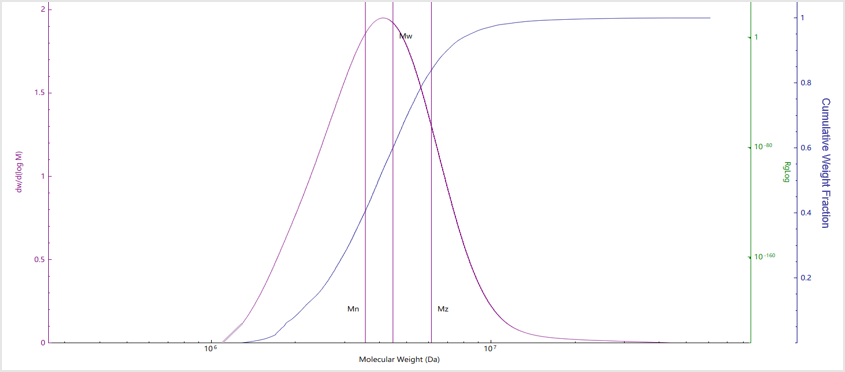
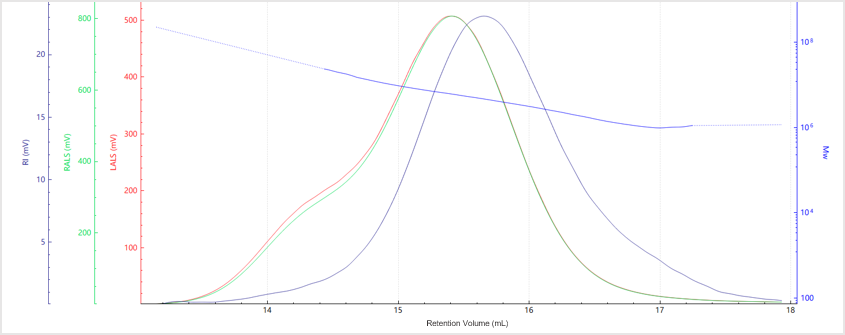
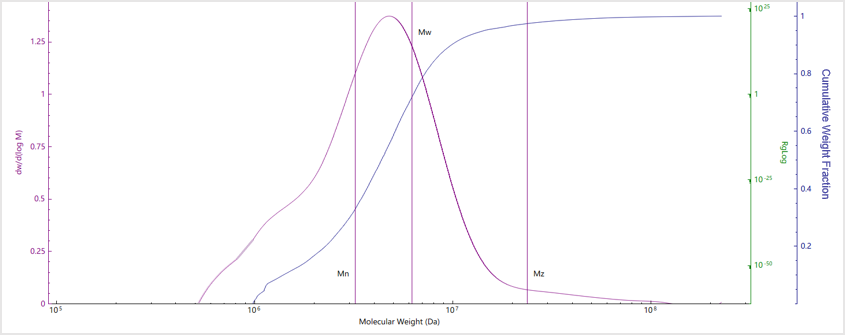
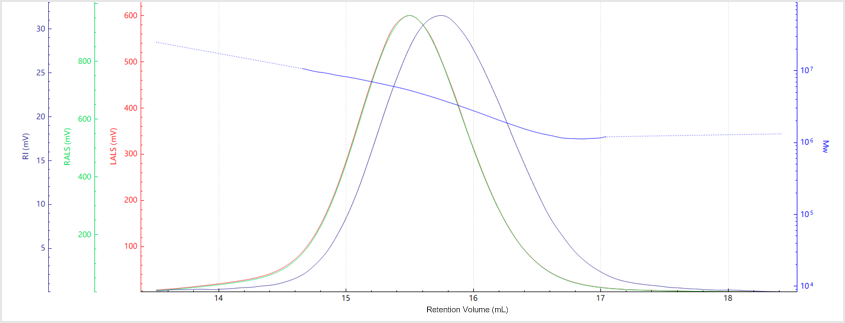
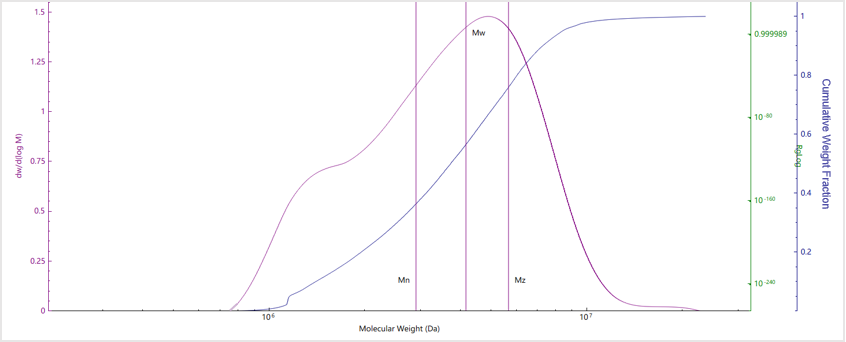
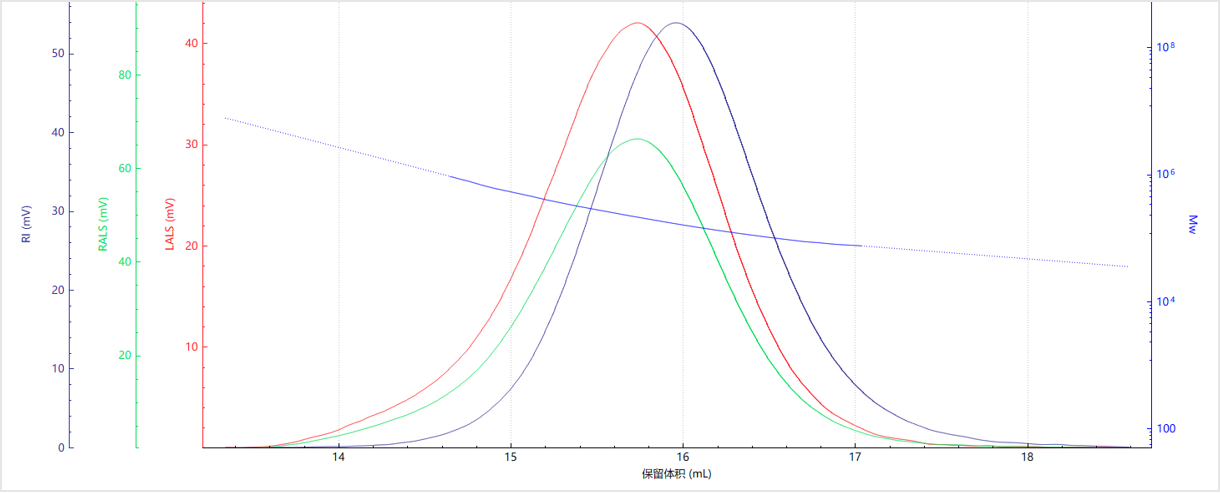
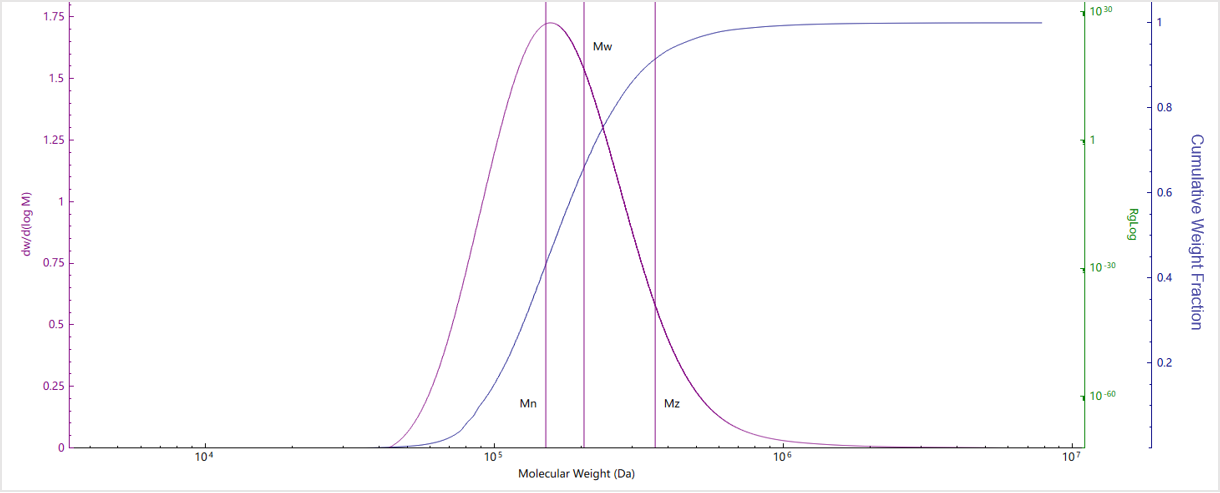
Results and Discussion
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
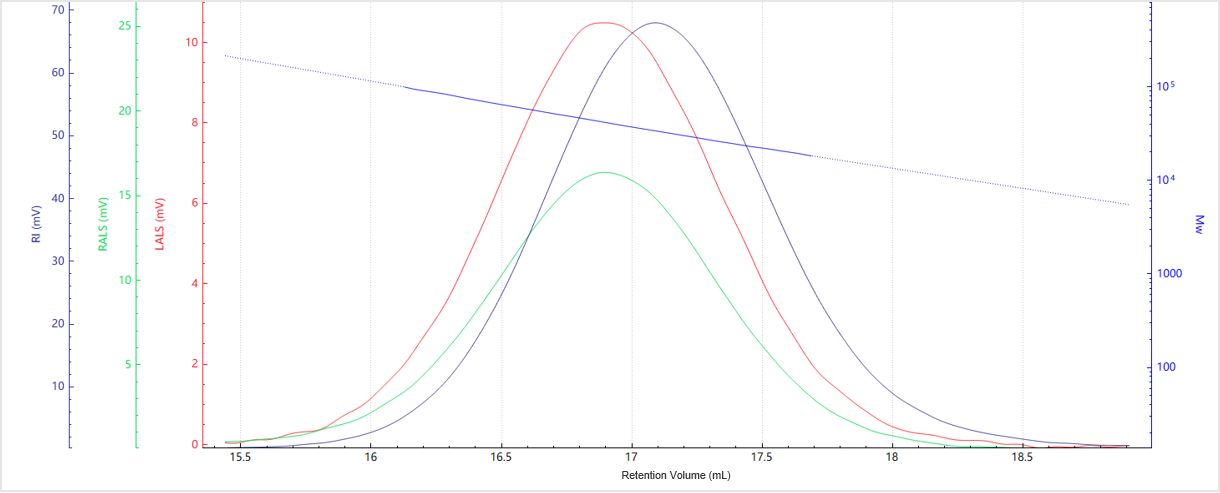 |
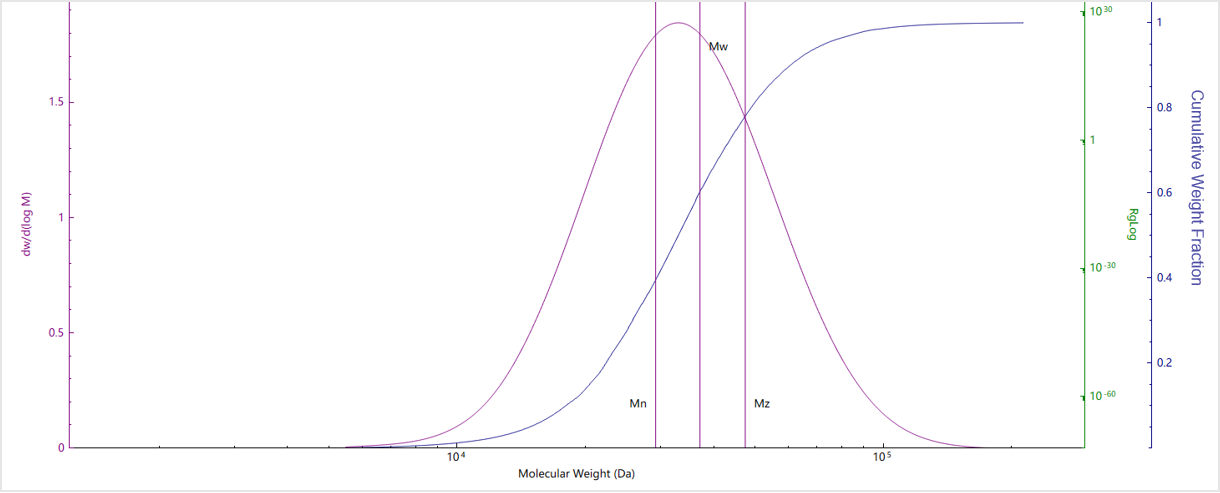 |
| No. | Mn (kDa) | Mw (kDa) | Mz (kDa) | Mw/Mn |
| Sample A | 3559 | 4465 | 6128 | 1.25 |
| Sample B | 3218 | 6222 | 23741 | 1.37 |
| Sample C | 2903 | 4168 | 5676 | 1.13 |
| Sample D | 150.8 | 204.5 | 360.45 | 1.3 |
| Sample E | 29.2 | 37.1 | 47.5 | 1.27 |
Conclusion
About the Authors
 |
Zhibin Guo |
Recommended articles
Rate this article
