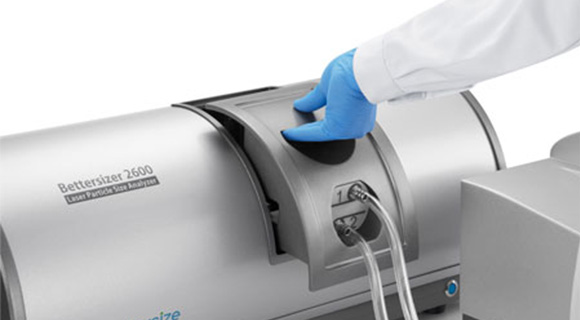
粒度分布測定装置ベターサイザー2600は、湿式・乾式どちらでも測定可能です。モジュラー設計と特許技術により、この多用途で強力な分析装置はさまざまなアプリケーションをカバーします。0.02μmから2600μmまでの材料を簡単かつ正確に特性評価できます。
機能と利点
- ● 技術レーザー回折
- ● 粒子径範囲湿式分散:0.02~2,600μm 乾式分散:0.1~2,600μm
- ● 湿式および乾式粒度分布測定法は、さまざまな分散粒子系に適しています。
- ● フーリエ光学系と逆フーリエ光学系の両方を利用した新しい特許技術により、広い範囲をカバーする大小両方の粒子を正確に測定。
- ● 0.016°~165°の角度範囲をカバーする92個の検出器を備えた光学ベンチ オプションの湿式/乾式分散器
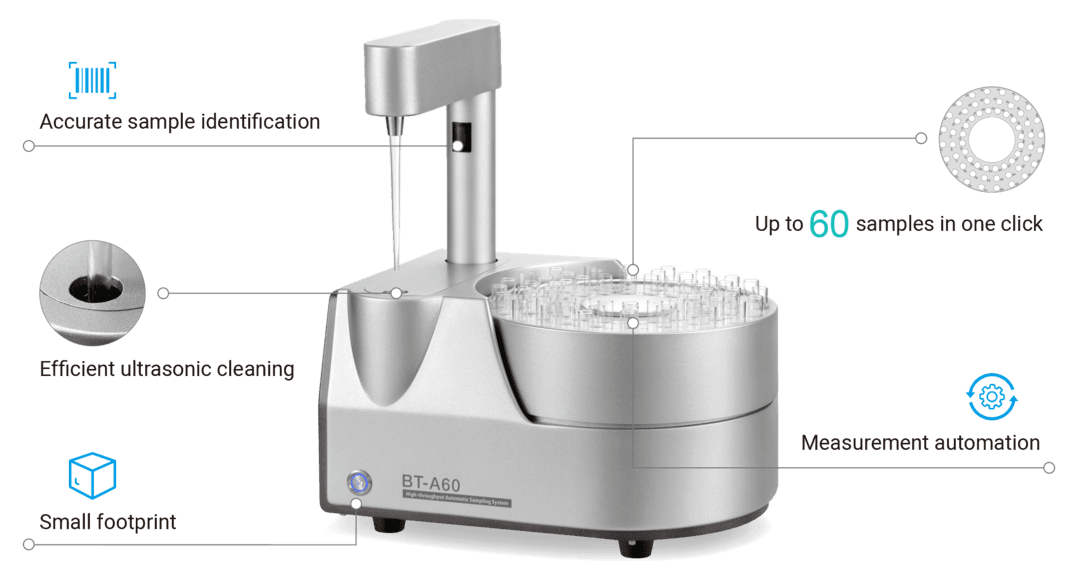
- ● 少量のサンプルに対応する少量乾式分散モジュール、特に医薬品や供給量の少ない貴重なサンプルに適しています。
- ● 分散モジュールの交換が簡単で速い
- ● 新素材の標準作業手順の導入、作成、使用が容易
- ● 屈折率測定により、より正確なパラメーターを算出。
- ● ユーザーフレンドリーなソフトウェア。
ビデオ
Bettersizer 2600 | Laser Diffraction Particle Size Analyzer (Wet & Dry) 
Snippet - How to Measure Particle Size of Coffee Powder 
How to Install and Operate Bettersizer 2600 
Ask an Expert! Introducing Bettersizer 2600 
A Brief Introduction to Laser Diffraction | Fundamentals of Bettersizer 2600 
Bettersizer 2600 Demonstration with Corundum (Al2O3) sample 
How to Measure Particle Size of Cosmetics 
How to Measure Particle Size of Coffee Powder 
Bettersizer 2600 Overview | Laser Diffraction Particle Size Analyzer (Dry & Wet Dispersions) 
概要
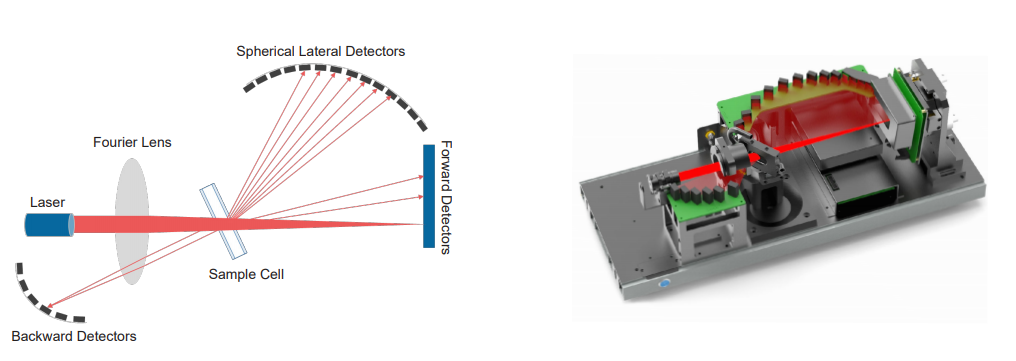
1.フーリエ光学系と逆フーリエ光学系
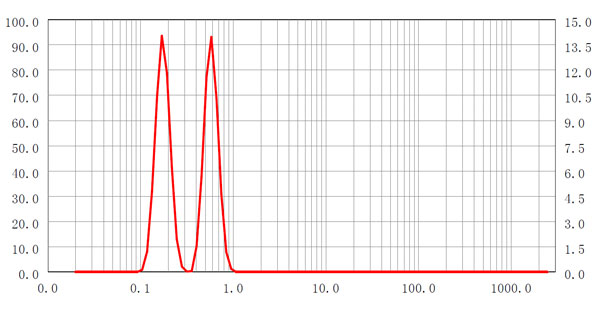
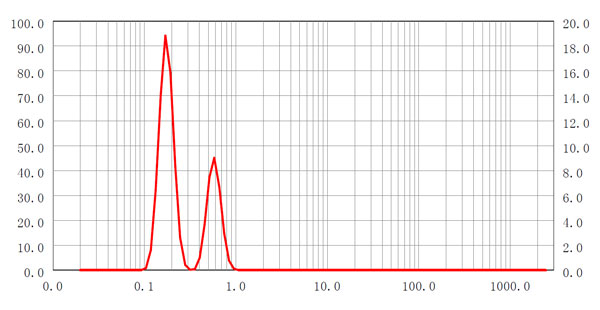
ベターサイザー2600は、フーリエ光学系と逆フーリエ光学系の組み合わせに優れています。このスマートな設計により、一方では0.016°から165°までの非常に広い角度範囲での散乱光の検出が可能になります。一方、逆フーリエ設計とは対照的に、粒子は一平面上にある必要はなく、小さな粒子と大きな粒子を同時に正確に測定することができます。
フーリエ・デザインと逆フーリエ・デザインの組み合わせの特徴
- 球状検出器アレイ:前方検出器、側方検出器、後方検出器、合計92個;
- 超大型フーリエレンズ
- 小さな設置面積:コンパクト設計で省スペース。
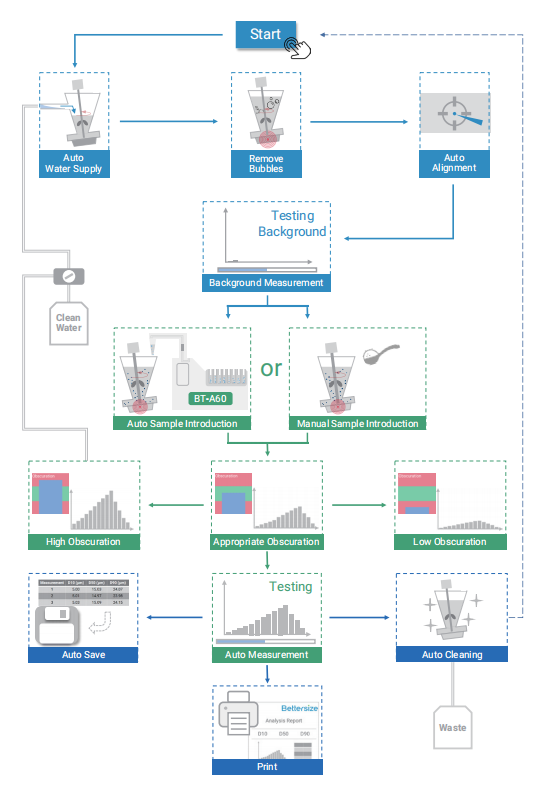
2.直感的で強力なソフトウェア
- 直感的なユーザーインターフェースと整然とした操作
- 最適な測定条件を決定するリアルタイムPSDカーブ
- 全自動測定ルーチン
- 自動クリーニング・ルーチン
- 自動データバックアップとカスタマイズ可能なレポート
- フラウンホーファーおよびMie評価モデルによる直接変換
- ワンクリックで湿式分散モジュールと乾式分散モジュールを切り替え可能
3.湿式分散
BT-802 は、水を媒体とした粒度分布測定用に設計されています。


| エタノール | メタノール | イソプロパノール | エーテル |
| トルエン | キシレン | ジクロロメタン | オクタン |
| 酢酸エチル | アセトン | オレイン酸メチル | NMP溶剤 |
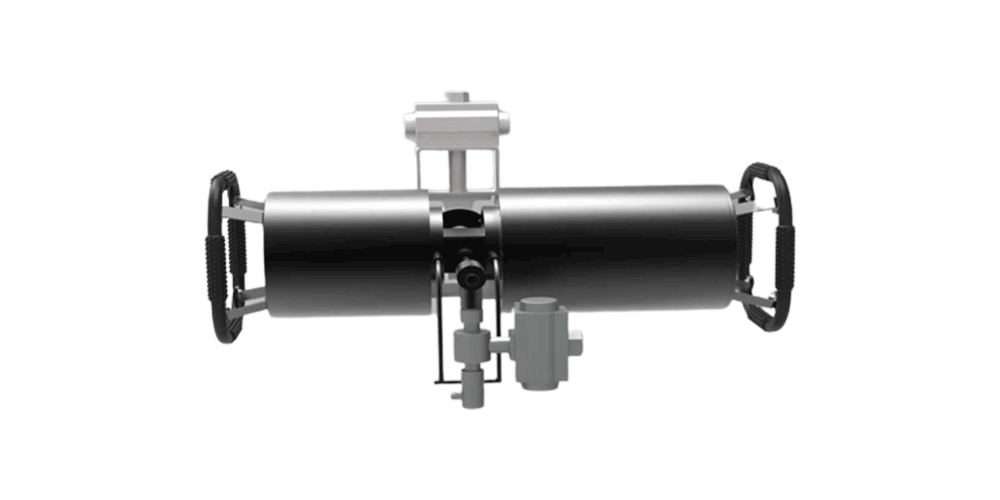
BT-80Nはステンレス製シェルで構成されています。遠心ポンプ、超音波分散器、PTFEパイプライン、焼結石英サンプルセル、制御回路などが含まれています。

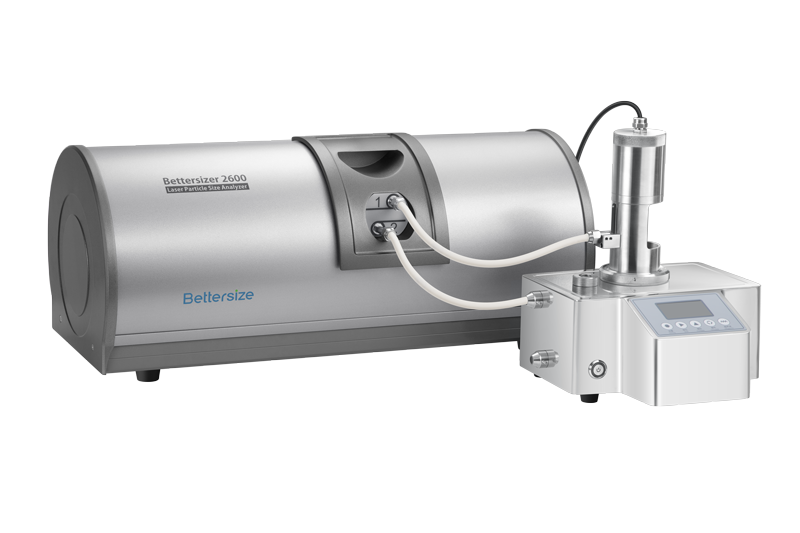

BT-804は、溶媒や水を媒体とする貴重なサンプルや少量のサンプル測定用に設計されています。モジュールは、ABSシェル、攪拌モーター、キュベット(8mL)、攪拌子などで構成されています。
- 最大容量は8 mLで、サンプル質量は0.005~0.1 gです。
- 水または有機相に分散したサンプルに適しています。


4.乾式分散
BT-902は乾燥粉末測定に適しています。使用するガスは圧縮空気、窒素、その他の希ガスです。
BT-902は電磁振動フィーダー、ベンチュリー管、ガス回路、電気回路、圧力センサー等で構成されています。




5.用途

Citations
- Bettersizer 2600
Functional redundancy as an indicator for evaluating functional diversity of macrobenthos under the mussel raft farm near Gouqi Island
DOI: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2023.740024 Read ArticleZhejiang Ocean University | 2024Biological traits analysis (BTA) helps to evaluate the effects of different environmental variables on the traits-based functional composition of macrobenthos. However, research on functional traits of macrobenthos under mussel farming is limited. We investigated the spatial and temporal response of the benthic system in terms of taxonomic and functional diversity to environmental variables of farming and natural stressors resulting from suspended mussel farming near Gouqi Island of eastern China Sea. The functional traits of macrobenthic assemblages under mussel farming were characterized by “medium adult body size”, “vermiform body form”, “high flexibility”, “infauna”, “semi-motile”, “gonochoristic”, “surface deposit-feeders”, “carnivores”, “semi-motile burrowers”, and “tube-dwellers”. Functional redundancy was stable in response to mussel farming stresses among seasons, whereas species diversity showed efficient to evaluate natural variables. Functional diversity was significantly affected by farming stressors rather than natural variables, Further analysis using multivariate methods together with continuous monitoring were highlighted to evaluate the impacts of mussel farming. Our results reinforce the importance of macrobenthic species and functional traits analysis to evaluate human stresses driven impacts in offshore ecosystems. By analysing the environmental variables with different sources, independently, we concluded the main effects of human pressures on macrobenthic community. Such distinction could be particularly effective to isolate variable environmental descriptors and evaluate their effects on functional diversity, making the current approach promising for the evaluation of ecological effects of anthropogenic stressors in aquaculture areas. - Bettersizer 2600
Degradation characteristics and utilization strategies of a covalent bonded resin-based solid amine during capturing CO2 from flue gas
DOI: 10.1016/j.seppur.2023.125621 Read ArticleChina University of Petroleum | 2024In this study, various types of degradation as well as attrition which are possibly encountered in a circulating fluidized bed temperature swing adsorption (CFB-TSA) process, were conducted experimentally to evaluate the stability of a resin-based solid amine sorbent. Other characterizations methods, such as elemental analysis (EA), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) etc. were applied to further reveal the degradation mechanisms. The results showed that thermal degradation occurs from 140–160 °C due to the decomposition of amine group. The CO2-induced degradation occurs from a higher temperature of 160–180 °C accompanied by the production of urea. Hydrothermal stability is good below 130 °C, but the ionic impurities in steam crystalized on particle surface can accelerate the degradation. Oxidative degradation is the most harmful, which starts at a lower temperature of 70–80 °C with the formation of aldehyde. The existence of H2O in atmosphere can alleviate the oxidative and CO2-induced degradations. The employed sorbent has a very low attrition index of 0.05, which is 1–2 orders lower than typical commercial fluidized bed catalysts. Based on the results of stability evaluation, some design suggestions for proper utilization of this sorbent or other similar resin-based sorbents have been provided in an industrial CFB-TSA process.
- Bettersizer 2600
De-branching of starch molecules enhanced the complexation with chitosan and its potential utilization for delivering hydrophobic compounds
DOI: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2023.109498 Read ArticleShihezi University | 2024The current study aimed to prepare the complexes between debranched-waxy corn starch and chitosan polymers (DBS-CS), and then investigated their corresponding structural characteristics, rheological property and potent application in Pickering emulsion. The results indicated that the existence of chitosan significantly inhibited starch short-range molecular rearrangement for all DBS-CS samples, which was manipulated by both debranching treatment and chitosan content. Interestingly, this is the first study to reveal that the outstanding peak at 1.8 ppm in 1H NMR spectrum for sample DBS-CS was gradually shifted towards a lower-field region following an increased chitosan content. Moreover, the debranching treatment shifted the crystallinity pattern from A-type to B-type and the relative crystallinity of DBS-CS decreased gradually with the increased content of CS. All samples had a pseudoplastic fluid and shear-thinning behavior with an enhanced shear resistance following the complexation. The DBS-CS was applied in a Pickering emulsion for showing a greater emulsifying stability and a lower gel strength than native NS-CS prepared emulsion. Importantly, the encapsulation ability of curcumin in the DBS-CS emulsion was significantly improved, followed by an increase of 15.45% for its corresponding bioavailability compared to the control. Therefore, this study might highlight a potential carrier for delivering the bioactive substances in a green pattern. - Bettersizer 2600
Heat-induced aggregation behavior of wheat gluten after adding citrus pectin with different esterification degree
DOI: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2023.109420 Read ArticleGansu Agricultural University | 2024Wheat gluten aggregation during heat treatment is beneficial to the final quality of gluten-based products. Exogenous pectin can affect gluten aggregation. However, the effect of pectin with different degrees of esterification on the heat-induced aggregation behavior of gluten and its possible mechanism are still unclear. Thus, the heat-induced aggregation behavior of gluten after adding pectin with different esterification degree was studied in this study. When the temperature was raised from 25 °C to 95 °C, pectin affected gluten aggregation and was related to the degree of esterification. Specifically, the results of rheological properties and particle size indicated that low-ester pectin improved the viscoelasticity of gluten and promoted gluten aggregation. Thermal properties revealed that enthalpy of gluten added with low-ester pectin (37%) increased from 92.96 J/g to 95.40 J/g during heating process. Structurally, the fluorescence intensity and surface hydrophobicity of gluten added with low-ester pectin (37%) were lower than those added with high-ester pectin (73%). In addition, low-ester pectin (37%) significantly increased the disulfide bond content (from 15.31 μmol/g to 18.06 μmol/g) and maintained β-sheet content of gluten compared with gluten alone at 95 °C, indicating that low-ester pectin was more likely to induce gluten aggregation. However, scanning electron microscope showed that the gluten added with low-ester pectin (46%) exhibited a denser network structure at 95 °C than that added with low-ester pectin (37%). These results will provide a theoretical base for the regulation of gluten aggregation and the quality of gluten-based products by pectin with different esterification degree.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 84
厳選されたリソース
お客様のお声