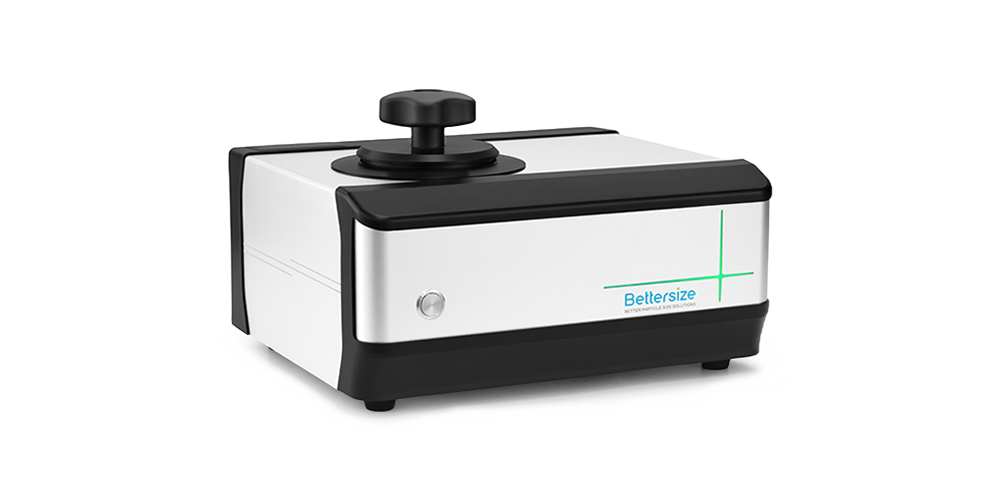
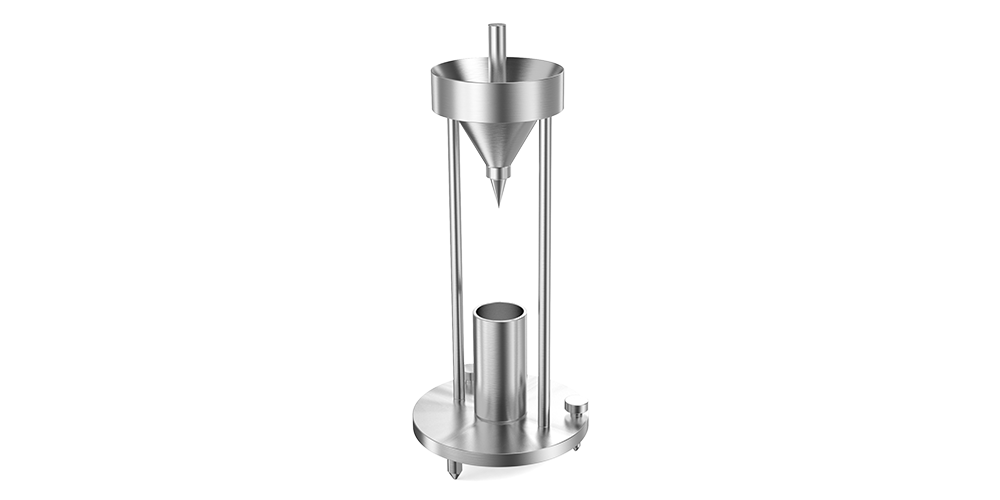
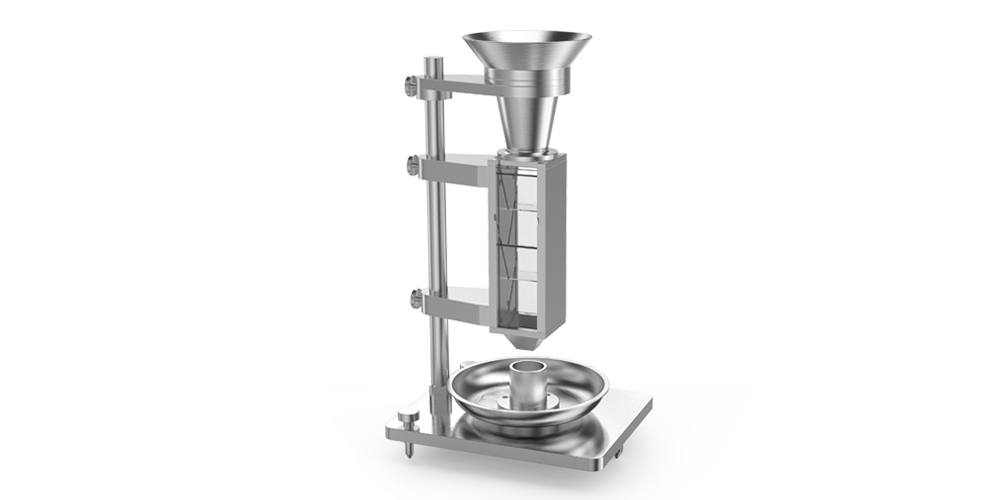
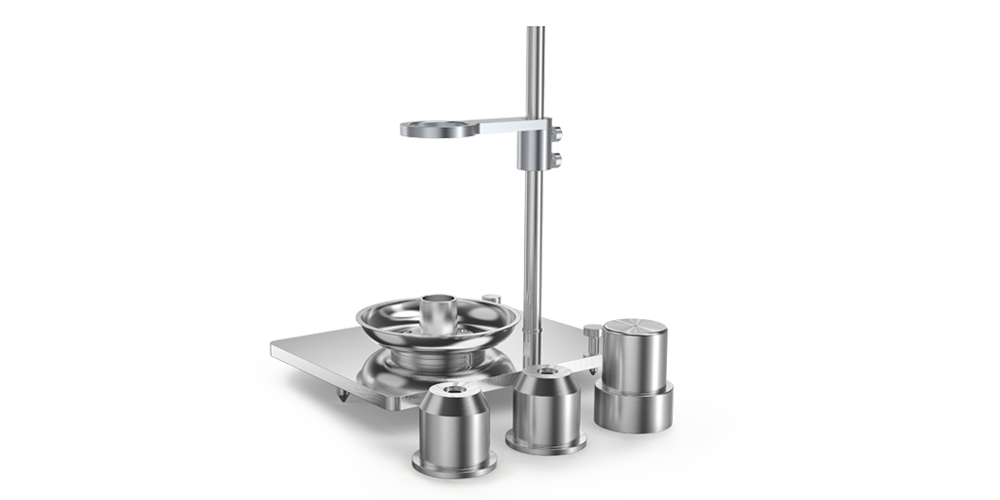
PowderPro A1
Le PowderPro A1 intègre de nombreuses technologies de pointe telles que le contrôle intelligent par Wi-Fi, la technologie de traitement de l'image et la technologie de vibration électromagnétique 3D. Il peut mesurer les propriétés physiques des poudres de manière rapide, simple et précise. En tant que testeur intelligent des caractéristiques des poudres, il s'agit d'un instrument essentiel pour vous aider à comprendre et à étudier les matériaux en poudre.
Caractéristiques et avantages
- ● Conception compacte
- ● Contrôles multiples
- ● Sortie de données pratique
- ● Transmission intelligente des données
- ● Technologie de contrôle automatisé
- ● Technologie d'imagerie automatisée
Vidéo
What is angle of repose? Why and how do we measure it? 
Flowability Calculation of Powder Materials Using PowderPro A1 
Cohesion & Uniformity Measurement and Calculation of Powder Materials Using PowderPro A1 
Tapped Density and Compressibility Measurement of Powder Materials Using PowderPro A1 
Bulk Density Testing of Non-metallic Powder Materials with PowderPro A1 
Angle of Spatula Measurement of Powder Materials with PowderPro A1 
Angle of Repose, Angle of Fall & Angle of Difference Testing of Powder Materials with PowderPro A1 
PowderPro A1 Overview | Automatic Powder Characteristics Tester 
Vue d'ensemble
Caractéristiques et avantages du testeur de caractéristiques physiques des poudres PowderPro A1
1) Paramètres mesurés et calculés
PowderPro A1 effectue des mesures entièrement automatiques :
- Angle de repos et de chute
- Angle de la spatule (angle du plateau)
- Densité apparente et densité de piquage
- Dispersibilité
- Vide et cohésion
PowderPro A1 calcule de manière entièrement automatique :
- Angle de différence
- Compressibilité
- Uniformité
- Indice de fluidité
- Indice d'inondabilité
- Taille du tamis
2) Mesure des angles par la méthode de l'image
Des photographies ont été prises à l'aide de la technologie d'imagerie CCD haute définition. Les paramètres tels que l'angle de repos, l'angle de chute et l'angle de spatule sont obtenus rapidement et facilement avec une grande précision et une bonne répétabilité grâce à la technologie unique de reconnaissance et de traitement des images.
3) Technologie brevetée de vibration rotative :
Assure une surface lisse de la poudre et améliore la précision des mesures.
4) Technologie de contrôle automatique :
La commande entièrement automatique par PC ou mobile garantit une utilisation et un fonctionnement faciles. Le mode SOP permet d'obtenir des résultats d'essai précis et fiables pour un processus d'essai normalisé.
5) Conformité :
- ISO 3953:1993
- USP 32-NF27<616>
- Ph. Eur.7.0 07/2010:20934E
6) Communication des données :
Une balance électronique est connectée à l'instrument et les données de poids sont automatiquement transférées au système pour le traitement des données et le calcul des résultats.
7) Technologie avancée de densité de prélèvement :
La densité de prélèvement est obtenue par la combinaison parfaite de la fréquence variable et de la technologie de vibration rotative. La fréquence de vibration de 50 à 300 fois par minute peut être réglée en continu ; l'amplitude de vibration de 3 ou 14 mm peut être sélectionnée. Pendant la vibration, le cylindre est en rotation uniforme, ce qui garantit l'horizontalité de la surface de la poudre et améliore la précision de la lecture.
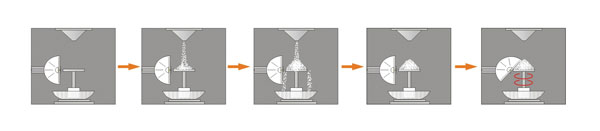
- Mesure de l'angle de repos
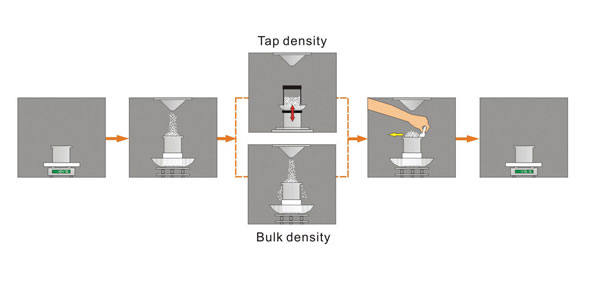
- Mesure de la densité en vrac et de la densité par piquage
Citations
- Bettersizer 2600
Functional redundancy as an indicator for evaluating functional diversity of macrobenthos under the mussel raft farm near Gouqi Island
DOI: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2023.740024 Read ArticleZhejiang Ocean University | 2024Biological traits analysis (BTA) helps to evaluate the effects of different environmental variables on the traits-based functional composition of macrobenthos. However, research on functional traits of macrobenthos under mussel farming is limited. We investigated the spatial and temporal response of the benthic system in terms of taxonomic and functional diversity to environmental variables of farming and natural stressors resulting from suspended mussel farming near Gouqi Island of eastern China Sea. The functional traits of macrobenthic assemblages under mussel farming were characterized by “medium adult body size”, “vermiform body form”, “high flexibility”, “infauna”, “semi-motile”, “gonochoristic”, “surface deposit-feeders”, “carnivores”, “semi-motile burrowers”, and “tube-dwellers”. Functional redundancy was stable in response to mussel farming stresses among seasons, whereas species diversity showed efficient to evaluate natural variables. Functional diversity was significantly affected by farming stressors rather than natural variables, Further analysis using multivariate methods together with continuous monitoring were highlighted to evaluate the impacts of mussel farming. Our results reinforce the importance of macrobenthic species and functional traits analysis to evaluate human stresses driven impacts in offshore ecosystems. By analysing the environmental variables with different sources, independently, we concluded the main effects of human pressures on macrobenthic community. Such distinction could be particularly effective to isolate variable environmental descriptors and evaluate their effects on functional diversity, making the current approach promising for the evaluation of ecological effects of anthropogenic stressors in aquaculture areas. - Bettersizer 2600
Degradation characteristics and utilization strategies of a covalent bonded resin-based solid amine during capturing CO2 from flue gas
DOI: 10.1016/j.seppur.2023.125621 Read ArticleChina University of Petroleum | 2024In this study, various types of degradation as well as attrition which are possibly encountered in a circulating fluidized bed temperature swing adsorption (CFB-TSA) process, were conducted experimentally to evaluate the stability of a resin-based solid amine sorbent. Other characterizations methods, such as elemental analysis (EA), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) etc. were applied to further reveal the degradation mechanisms. The results showed that thermal degradation occurs from 140–160 °C due to the decomposition of amine group. The CO2-induced degradation occurs from a higher temperature of 160–180 °C accompanied by the production of urea. Hydrothermal stability is good below 130 °C, but the ionic impurities in steam crystalized on particle surface can accelerate the degradation. Oxidative degradation is the most harmful, which starts at a lower temperature of 70–80 °C with the formation of aldehyde. The existence of H2O in atmosphere can alleviate the oxidative and CO2-induced degradations. The employed sorbent has a very low attrition index of 0.05, which is 1–2 orders lower than typical commercial fluidized bed catalysts. Based on the results of stability evaluation, some design suggestions for proper utilization of this sorbent or other similar resin-based sorbents have been provided in an industrial CFB-TSA process.
- Bettersizer 2600
De-branching of starch molecules enhanced the complexation with chitosan and its potential utilization for delivering hydrophobic compounds
DOI: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2023.109498 Read ArticleShihezi University | 2024The current study aimed to prepare the complexes between debranched-waxy corn starch and chitosan polymers (DBS-CS), and then investigated their corresponding structural characteristics, rheological property and potent application in Pickering emulsion. The results indicated that the existence of chitosan significantly inhibited starch short-range molecular rearrangement for all DBS-CS samples, which was manipulated by both debranching treatment and chitosan content. Interestingly, this is the first study to reveal that the outstanding peak at 1.8 ppm in 1H NMR spectrum for sample DBS-CS was gradually shifted towards a lower-field region following an increased chitosan content. Moreover, the debranching treatment shifted the crystallinity pattern from A-type to B-type and the relative crystallinity of DBS-CS decreased gradually with the increased content of CS. All samples had a pseudoplastic fluid and shear-thinning behavior with an enhanced shear resistance following the complexation. The DBS-CS was applied in a Pickering emulsion for showing a greater emulsifying stability and a lower gel strength than native NS-CS prepared emulsion. Importantly, the encapsulation ability of curcumin in the DBS-CS emulsion was significantly improved, followed by an increase of 15.45% for its corresponding bioavailability compared to the control. Therefore, this study might highlight a potential carrier for delivering the bioactive substances in a green pattern. - Bettersizer 2600
Heat-induced aggregation behavior of wheat gluten after adding citrus pectin with different esterification degree
DOI: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2023.109420 Read ArticleGansu Agricultural University | 2024Wheat gluten aggregation during heat treatment is beneficial to the final quality of gluten-based products. Exogenous pectin can affect gluten aggregation. However, the effect of pectin with different degrees of esterification on the heat-induced aggregation behavior of gluten and its possible mechanism are still unclear. Thus, the heat-induced aggregation behavior of gluten after adding pectin with different esterification degree was studied in this study. When the temperature was raised from 25 °C to 95 °C, pectin affected gluten aggregation and was related to the degree of esterification. Specifically, the results of rheological properties and particle size indicated that low-ester pectin improved the viscoelasticity of gluten and promoted gluten aggregation. Thermal properties revealed that enthalpy of gluten added with low-ester pectin (37%) increased from 92.96 J/g to 95.40 J/g during heating process. Structurally, the fluorescence intensity and surface hydrophobicity of gluten added with low-ester pectin (37%) were lower than those added with high-ester pectin (73%). In addition, low-ester pectin (37%) significantly increased the disulfide bond content (from 15.31 μmol/g to 18.06 μmol/g) and maintained β-sheet content of gluten compared with gluten alone at 95 °C, indicating that low-ester pectin was more likely to induce gluten aggregation. However, scanning electron microscope showed that the gluten added with low-ester pectin (46%) exhibited a denser network structure at 95 °C than that added with low-ester pectin (37%). These results will provide a theoretical base for the regulation of gluten aggregation and the quality of gluten-based products by pectin with different esterification degree.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 84
Ressources sélectionnées
Analyseur de caractéristiques des poudres apparenté
-
BetterPyc 380
Gas Pycnometer
Technology: Gas Displacement Method
Temperature Range: 10 - 65 ℃
Resolution: 0.0001 g/cm³
-
BeDensi T Pro Series
Tapped Density Tester with a Wallet-Friendly Solution
Number of Workstations: 1-3
Tapping Speed: 100 - 300 taps/min
Repeatability: ≤1% variation
-
BeDensi B1
Bulk Density Tester
Measurement: Bulk Density
Compliance with GB/T 16913
-
BeDensi B1-S
Scott Volumeter
Measurement: Bulk Density
Compliance with USP, Ph. Eur., ASTM, and ISO standards
-
HFlow 1
Flowmeter Funnel
Measurement: Bulk density and Flow rate
Compliance with USP, Ph. Eur., ASTM, and ISO standards